Currently, only one CBD product called Epidiolex is approved to treat seizures in specific syndromes.
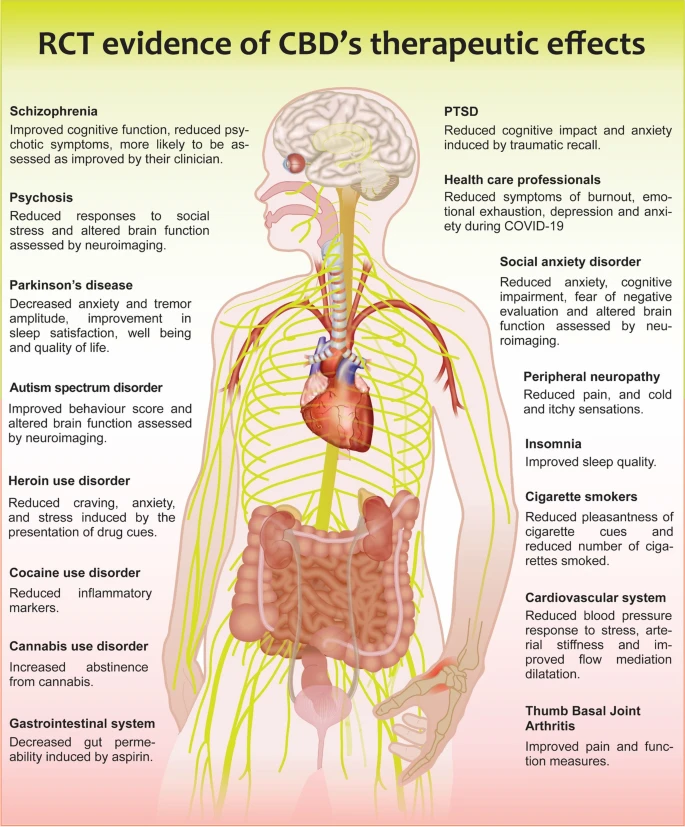
This review highlights the areas where purified CBD has the most clinical evidence for its potential benefits.
These include:
- Anxiety (positive data from 24 different studies)
- Psychosis and schizophrenia (positive data from 9),
- PTSD (positive data from 6), and
- Substance abuse (positive data from 5 ).
CBD taken orally in a single dose was found effective in reducing anxiety related to public speaking. It also contributed to the extinction of traumatic memories.
According to functional brain imaging studies, CBD may have anxiolytic effects since it decreased brain activity in areas of the brain linked to fear and anxiety.
Both an acute and a seven-day oral CBD treatment in healthy males decreased resting blood pressure and blood pressure response to stress.
The most current research on healthy volunteers, however, did not find any measurable anxiolytic effects of CBD. It is important to note that most of the participants in these experiments were female, and new preclinical data show the anxiolytic effects of CBD may be stronger in male rats.
The effects of CBD on anxiety were examined in several trials. While some produced unfavorable findings, individuals with Parkinson’s disease, heroin use disorder, and generalized social anxiety disorder (SAD) all reported beneficial outcomes.
In these patients, CBD was found to reduce cravings, anxiety brought on by public speaking, negative assessment, cognitive impairment, and subjective anxiety.
In conclusion, there is conclusive evidence that a single dose of CBD can reduce blood pressure and anxiety in healthy volunteers.
CBD has shown promising preliminary in SAD patients and has produced mixed results in anxiety associated with substance abuse and other conditions.
Ongoing trials are investigating the effects of CBD in various conditions, such as SAD, pediatric epilepsy, advanced breast cancer, anorexia nervosa, bipolar disorder, and Alzheimer’s disease, which will contribute to the growing evidence base on the use of CBD for anxiety-related conditions.
The review notes, also, that there is limited evidence or lack of support for the use of purified oral CBD in pain management (especially as an acute analgesic), the treatment of COVID symptoms, cancer, Huntington’s disease, or type 2 diabetes.
As usual, to establish the efficacy of purified CBD in various indications, larger trials are needed.
O’Sullivan, S.E., Jensen, S.S., Nikolajsen, G.N. et al. The therapeutic potential of purified cannabidiol. J Cannabis Res 5, 21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-023-00186-9
Comments
Post a Comment