Taking Vitamin B6 Can Help Reduce Anxiety and Depression, Research Shows
Newsweek
"To make this a realistic choice, further research is needed to identify other nutrition-based interventions that benefit mental well-being, allowing ...
No Evidence That Depression Is Caused by Low Serotonin Levels - Neuroscience News
Neuroscience News
2 Comments · Rajoo Ananth says: July 20, 2022 at 2:18 pm. Law suits galore will visit every Psychiatrist who made a living on long term mental health ...
Depression Linked to Consuming an Inflammatory Diet and Increasing Risk of Frailty
Neuroscience News
Middle-aged and older adults with depression may be more vulnerable to the effects of dietary inflammation, increasing the risk of frailty and ...
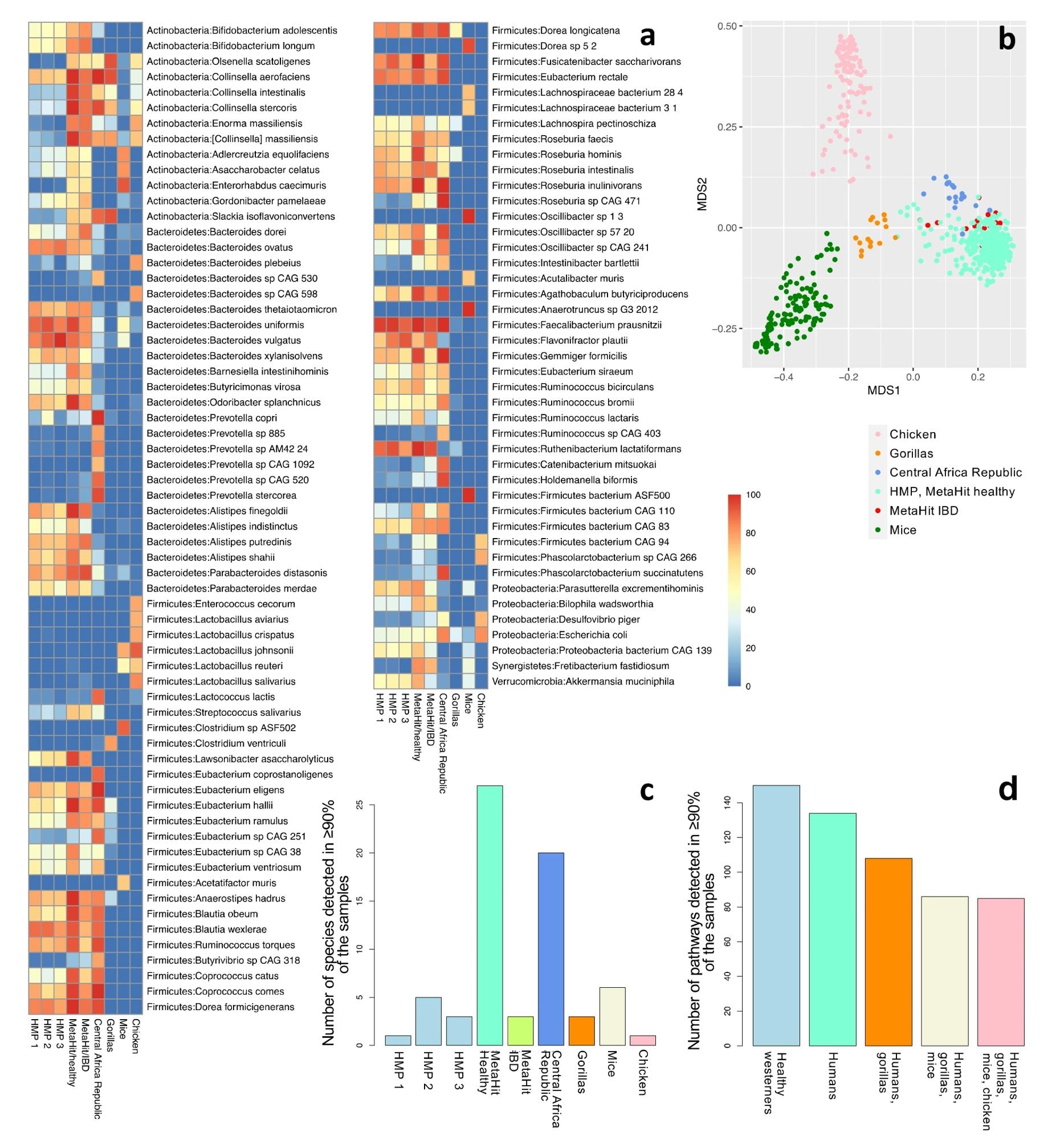
Identifying a core human microbiome - News-Medical
News-Medical
In a recent Nutrients journal study, researchers provide a critical review of the concept of 'the core human microbiome.
The #1 Best Berry for Weight Loss, Says Dietitian - Eat This, Not That
Eat This, Not That
"Fiber is one essential nutrient you need to include more of in your diet when you are looking to lose weight," explains Ehsani. "Berries provide ...
Comments
Post a Comment